Polynomial interpolation is a method of estimating values between known data points using polynomials. Given a set of data points, the goal is to find a polynomial that passes through all of these points.
# some libs
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.interpolate import interp1d
import numpy as npNewton’s Forward Interpolation¶
Let’s define for the first 3 differences,
def forward(x, y, x_n):
arr = [y]
for i in range(3):
temp = []
for j in range(0, len(arr[-1])-1):
temp.append(arr[-1][j+1] - arr[-1][j])
arr.append(temp)
print(arr)
h = (x_n - x[0]) / (x[1] - x[0])
a = arr[0][0]
b = h * arr[1][0]
c = h * (h-1) / 2 * arr[2][0]
d = h * (h-1) * (h-2) / 6 * arr[3][0]
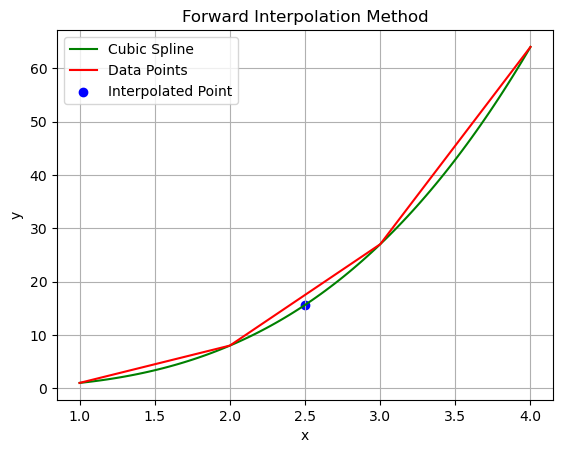
return a + b + c + dx = [1, 2, 3, 4]
y = [1, 8, 27, 64]
x_n = 2.5
y_n = forward(x, y, x_n)
x, y = np.array(x), np.array(y)
fn = interp1d(x, y, kind='cubic')
x_new = np.linspace(x.min(), x.max(), 100)
y_new = fn(x_new)
plt.plot(x_new, y_new, label='Cubic Spline', color='green')
plt.plot(x, y, color='red', label='Data Points')
plt.scatter(x_n, y_n, color='blue', label='Interpolated Point')
plt.title('Forward Interpolation Method')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()[[1, 8, 27, 64], [7, 19, 37], [12, 18], [6]]
Newton’s Backward Interpolation¶
Same as before, but using backward differences. Try it yourself!
Lagrange Interpolation¶
Lagrange interpolation is another method for polynomial interpolation that constructs a polynomial that passes through a given set of points.
def lagrange(x, y, x_n):
n = len(x)
res = 0
for i in range(n):
temp = y[i]
for j in range(n):
if i != j:
temp *= x_n - x[j]
temp /= x[i] - x[j]
res += temp
return res
y_n_lagrange = lagrange(x, y, x_n)
print(f"Lagrange Interpolated value at x = {x_n} is y = {y_n_lagrange}")Lagrange Interpolated value at x = 2.5 is y = 15.625